Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), Principle of EDM, Applications of Electrical Discharge Machining, Advantages of Electrical Discharge Machining, Limitations of Electrical Discharge Machining, Di-electric Fluid, Characteristics of Di-electric Fluid
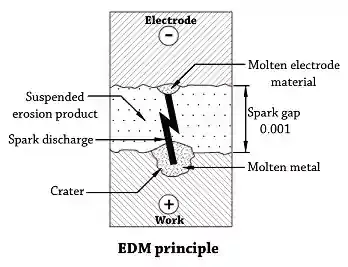
Principle of EDM:
This process is also called as spark machining or spark
erosion machining. EDM is a process of metal removal based on the principle of
erosion of metals by an interrupted electric spark discharge between the
electrode tool [usually cathode] and the work [anode]. If anode and cathode are
of the same material, it has been found that greater erosion takes place at
anode [positive electrode].
Therefore, in EDM process, work is made anode and
the tool is made cathode[-ve]. The tool and work are slide by the servo -
mechanism connected to the D.C supply circuit. This servo-mechanism is to
maintain a very small gap, i.e., spark gap (0.025 to 0.5 mm] between the tool
and the work. The D.C power supply is fed to the spark generating circuit. When
the potential difference [voltage] across the gap becomes sufficiently large,
the dielectric fluid becomes ionized and breaks down to produce an electrically
conductive spark between the work and tool. When the voltage drops below 12
volts, the spark discharge will extinguish and the di-electric fluid will
de-ionized. If the voltage becomes sufficiently large then, the tool and work
starts to recharge and the process repeats itself. This spark occurs in an
interval of 10 to 30 microseconds. Thus thousands of spark discharge occur per
second across the gap between tool and work, which result in a local
temperature of approximately 10000°C. This heat melts the workpiece and tool
and partially vaporized, thus the metal is removed from the work piece. The
time interval between the sparks is so short that the heat is unable to conduct
into the tool and work.
Applications, Advantages & Limitations of Electrical Discharge Machining
Applications of Electrical Discharge Machining:
• Manufacturing and re-conditioning of press tools and
forging dies.
• Injection moulding dies.
• Intricate and regular shaped profiles.
• For drilling micro holes.
• Diesel fuel injectors.
Advantages of Electrical Discharge Machining:
• Rapid rate of metal removal.
• Hard and tough materials can be machined [tungsten
carbides ceramics].
• Complex shapes can be machined.
• Disc electrode or wheel shape tools may be used.
• Absence of mechanical force makes it possible to machine
most fragile components.
• Holes of 0.005 mm can be produced in small delicate parts
using a very fine wire as tool.
• Gives good surface finish.
• Employed in manufacture and reconditioning of process
tools, forging dies and moulds used in injection moulding.
• Used for thread cutting , micro hole drilling and helical
profile drilling etc.
Limitations of Electrical Discharge Machining:
• Electrically non conducting materials cannot be machined
by EDM machine.
• It is normally well suited for small sized components.
• Possibility of developing micro cracks on machined
surfaces.
• Tool wear limits the degree of accuracy.
• Process is slow compared to conventional methods.
Di-electric Fluid & it's Characteristics
Di-electric Fluid:
A dielectric fluid is a medium that does not conduct electrically.In EDM process, the functions of dielectric fluid are:
• It acts as an insulating medium.
• It cools the spark region and helps in keeping the tool and workpiece cool.
• It maintains a constant resistance across the gap.
• It carries away the eroded metal particles.
Characteristics of Di-electric Fluid:
• Should have low viscosity.
• Should have reasonably safe flash point with maximum available positive ions [the passage of current necessitates positive ions].
END










0 Comments