Rolling, Hot Rolling, Cold Rolling, Two high Rolling Mill [Irreversible], Two High Rolling [Reversible], Three High Rolling, Four High Rolling, Cluster Rolling, Planetary Rolling, Terminology for Rolled Products
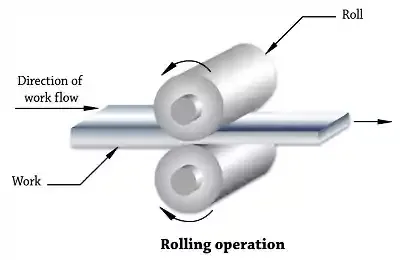
Principle of Rolling:
Compressing the metal between two opposite rotating rolls
for reducing its thickness - flat strip rolling. High compressive force is
exerted on the work piece by the squeezing action of the rolls. The metal is
taken into rolls by friction. It is most widely used due to higher productivity
at low cost. It is hot working process unless specifically mentioned as cold
rolling but it is done both hot and cold.
Hot Rolling:
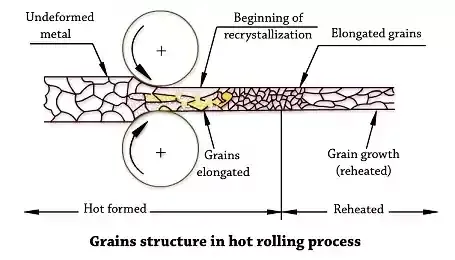
The hot plastic state metal is passed between rolls. Rolling
carried out above the recrystallization temperature. The crystals are elongated
in the direction of rolling, they start to reform after leaving the stress
zone. Best suited for large amount of deformation. Hot rolled metal is
generally free of residual stress and its properties are isotropic.
Cold rolling:
The rolling process employed to finish bars, rods, sheets
and strips at room temperature. It provides good surface finish, better
dimensional accuracy and improved physical properties. The crystals which are
elongated will retain substantially the shape given to them by the rolling
action.
Types of rolling mills:
1.Two high rolling mill [irreversible]
2.Two high rolling [reversible]
3.Three high rolling
4.Four high rolling
5.Cluster rolling
6.Planetary rolling.
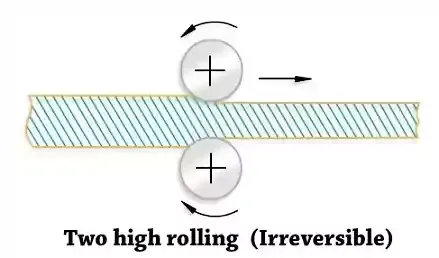
Two high rolling mill:
It has two rolls which rotates in same direction about the
horizontal axes.
The stock is returned to the entrance of the rolls for
successive reductions. The stock returned by hand or by a platform. This method
of reduction slow down the process. Typical two high rolling mill consists of a
roller conveyor, rolls with a stand and power drive. The upper roller can be
raised or lowered to change the distance between rolls. Alternate method is
used to fast the process where the direction of rolls is reversed after the
each pass - Two high rolling [reversible].
The rolls are brought close together for each pass. The
rolls in these mills have diameters ranging from 0.6 to 1.5 m. More power
consumption than irreversible two high rolling mill. It is often used for first
rolling operation. Applicable for both hot and cold rolling.
Three high rolling mill:
There are three rolls in the vertical column used for two
continuous process.
The direction of rotation of each rolls remains unchanged.
Stock is passed through the either side of the rolls. It is raised and lowered
after each pass using lifting mechanism. The top and bottom rolls are drive
rolls. Intermediate roll rotates by friction. These mills are employed as
blooming mills, billet rolling and finish rolling .More complicated due to
lifting mechanism.
Four high rolling mill:
Similar to two high rolling, but additional two rollers are
added.
These extra two rollers are smaller in diameter. Thus the
bigger roller will act as backup rollers behind smaller rollers. The arc of
contact is minimised by using smaller rollers. The backup rolls are provided to
avoid bending of rolls due to their low strength and rigidity.
Terminology for Rolled Products:
The various rolled products are given names according to the
dimensions, but the terminology is fairly loose and sharp limits with respects
to dimensions can not be made.
Bloom:
A bloom is the product of the first break down of ingot. It
has square or slightly rectangular section, ranging in size from 150 mm X 150
mm to 250 mm x 300 mm. A bloom is used to make structural shapes, that is, I
beams, channels etc.. by hot rolling.
Billet:
A reduction of bloom by bot rolling results in a billet. The
size of a billet ranges from 50 mm X 50 mm to 125 mm x 125 mm. It is rolled to
make rounds, wires and bars.
Slab:
A slab is a product obtained by bot rolling, either from
ingot or from bloom. It has a rectangular cross-section, with thickness = 50 to
150 mm and width = 0.6 to 1.5 m. Slabs are further rolled to get plates,
sheets, strips, coil etc.
Plate:
A plate is a finished or semi-finished product with a
minimum thickness of 6.35 mm Its width will be equal to the width of the roll
and the length equal to the maximum which can be handled or shipped.
Sheet:
A sheet is a thin partner of plate with a maximum thickness
of 6.35 mm.
Strip:
A strip is a narrow sheet and has a maximum width of 600 mm
with a maximum thickness of 6.35 mm. Since it is normally handled in coil form,
its length can be considerable and is limited only by the manufacturing and
handling facilities.
Foil:
It is a thin strip with a maximum width of 300 mm and a
maximum thickness of 1.5 mm. It is available in coil form.
Bar:
It is a long, straight, symmetrical piece of uniform cross
section. It may be round, square or of another configuration. A circular bar is
called a rod.
Wire:
A wire is a thin variety of bar, available in coil form and
not normally so identified over 9.5 mm cross-section.
END











0 Comments