Flexible manufacturing system or FMS, Definition of FMS, Features of FMS, Necessity of FMS, Objectives of FMS, Components of FMS, Production equipment, Types of FMS layout, Working of FMS, Advantages of FMS, Disadvantages of FMS
Flexible Manufacturing System [FMS]:
• FMS - Flexible manufacturing system.• A flexible manufacturing system is a highly automated group technology cell.
• FMS consists of a group of processing work stations interconnected by an automated material handling and storage system and controlled by computer system.
Definition of FMS:
• FMS is a manufacturing system based on multi operation machine tools, incorporating integrated computer control with associated support function of automatic material handling.
• FMS covers a wide
middle territory with in the mid volume, mid variety production range.
• It is designed to produce a medium part variety and medium production rate in the CIMS.
• So the FMS is considered to be a subset of CIMS.
• FMS become necessary for producing parts with medium range production and flexible in manufacturing.
• It is designed to produce a medium part variety and medium production rate in the CIMS.
• So the FMS is considered to be a subset of CIMS.
• FMS become necessary for producing parts with medium range production and flexible in manufacturing.
Features of FMS:
●
FMS has the capability
of producing different parts without major retooling.
●
It has the capability of
producing large volumes of a product at a lower cost, but very inflexible in
terms of the product types which can be produced.
●
FMS are able to change a
production schedule, to modify a part or to handle multiple parts.
●
Ability to adapt to
engineering changes in parts.
●
Increase in number of
similar parts produced on the system.
●
Ability to accommodate
routing changes.
●
Ability to rapidly
change production set up.
●
FMS is distinguished
from an automated production line by its ability to process more than one
product style simultaneously.
●
At any moment, each
machine in the system may be processing a different part type. FMS can let us
make changes in production schedule in order to meet the demands on different
products.
●
New product styles can
be introduced into production with an FMS, so long as they are to be used on
the products that the system can process.
Therefore, this kind of system is ideal, when there are
likely to be changes in demands.
Necessity of FMS:
● To improve operational control through,
» Reduction in the number
of uncontrollable variables.
» Providing tools to
recognize and react quickly to deviations in the manufacturing plan.
» Reducing the dependence
of human communication.
● To reduce direct labour,
» Removing operators from
the machining site.
» Eliminating dependence
on highly skilled machines.
● To improve short run responsiveness consisting of,
» Engineering changes
» Processing changes
» Machining downtime or
unavailability
» Cutting tool failure
» Late material delivery
● To improve long-run
accommodations through quicker and easier assimilation of,
» Changing product volume
» New product additions and
introductions
» Increases machine
utilization.
Objectives of FMS:
A study, carried out with West Germany manufacturing has shown the major aims of installing an FMS to be:• Decreased lead times
• Increased machine utilization
• Improved due rate reliability
• Decreased store inventors levels
• Decreased work in progress
• Increased quality.
Components of FMS:
The major components of a FMS are;• Production equipment
• Support systems
• Materials handling system
• Automated storage and retrieval system
• Buffer storing of parts
• Chip removal and washing stations
• Computer control system.
Production equipment:
The work centres used in sheet metal FMS include turret punch presses, laser machining centres, press brakes, sheet stacking system, loading and unloading device, sorting conveyor etc. FMS uses the number of special purpose machine and CNC machining centre for unique operation.Support systems:
• Automated machine tools require several systems to support their operation.• The tools required to perform the multiple processes of a machining centre may be stored in magazines at each machine or in a central tool storage.
• Centralization allows the total number of tools to be minimized and supports measuring tools for wear, tool presetting, tool repair and maintenance and replacement.
• Elaborate tool management software is an integral part of FMS software.
Material handling system:
• A FMS consists of several material handling systems that have to be synchronized with the machine operations.• The location and movement of workpieces are tracked automatically by using sensors on the material handling system and work stations.
• Automated guided vehicle [AGV) is the widely used type material handling device in a FMS.
• These are
battery-powered vehicles that can move and transfer materials by following
prescribed paths around the manufacturing floor.
• AGV's have on-board controllers that can be programmed for complicated and varying routes as well as load and unload operations.
• The computer provides overall control functions, i.e., dispatching, routing, traffic control and collision avoidance.
• AGV's have the flexibility for complex and programmable movement around the manufacturing shop.
• AGV's are safe as they are incorporated with warning lights, fire safety interlocks and bumpers.
» Storage structure
» Storage and retrieval machine
» Storage modules
» Pick-up and deposit stations.
• Some of the special features of AS/RS are transfer cars, full/empty bin detectors, sizing stations, load identification stations etc.
• AGV's have on-board controllers that can be programmed for complicated and varying routes as well as load and unload operations.
• The computer provides overall control functions, i.e., dispatching, routing, traffic control and collision avoidance.
• AGV's have the flexibility for complex and programmable movement around the manufacturing shop.
• AGV's are safe as they are incorporated with warning lights, fire safety interlocks and bumpers.
Automated storage and retrieval systems [AS/RS]:
• An automated storage and retrieval systems [AS/ RS] operations are controlled by a computer AS/RS consists of;» Storage structure
» Storage and retrieval machine
» Storage modules
» Pick-up and deposit stations.
• Some of the special features of AS/RS are transfer cars, full/empty bin detectors, sizing stations, load identification stations etc.
Buffer storing of parts:
• In a FMS, parts go from one work cell to another work cell, where various processing tasks are to be performed.• Because of the random production facilities of FMS, the destination cell might not always be ready to accept the incoming part and the part has to wait in a buffer store.
• Buffer stores for parts are always required, as there are dislocations in the in- process materials handling and transportation system.
Chip removal and washing stations:
• Workpiece cleaning is important especially before the part goes to the inspection station or assembly station.• The swarf removal is done at the washing station of the FMS.
• The pallet with fixtured-part is loaded onto the washing station, is tilted by a hydraulic mechanism, while being rinsed under high pressure coolant or pressurised air supply.
• While reverting to its load/unload position, the pallet is blown clean with compressed air.
• The cleaned part is transported/transferred by a robot or AGV together with its pallet.
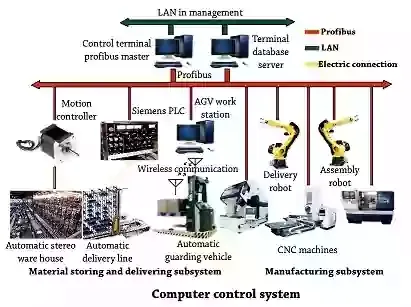
Computer control system:
• It is used to integrate the sub-systems in an FMS.• Other systems like CNC machines, monitoring and sensing devices, data communication and data collection system, programmable logic controller etc., are also controlled and integrated by a LAN network of computers.
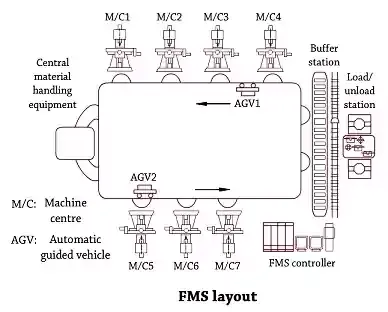
Types of FMS layout:
Flexible manufacturing system brings rewards in actual manufacture of products as the process is designed for several products to be run different machines within a manufacturing facility in the output. A Flexible manufacturing system is designed to provide an effective operation sequence to fulfill the production requirements and reasonably allocate the resources. The objectives of the system are to shorten the throughput time and reduce the resource requirements which include avoiding deadlock in material flow, decreasing in process inventory, balancing the workload of all machines and make good use of the bottleneck devices.Types of FMS layouts are;
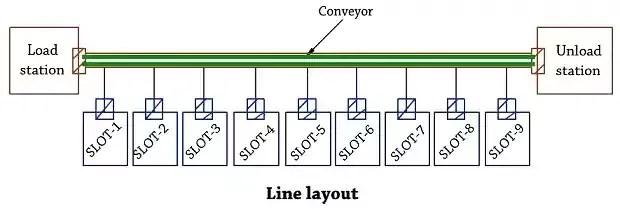
• In-line layout
• Loop layout
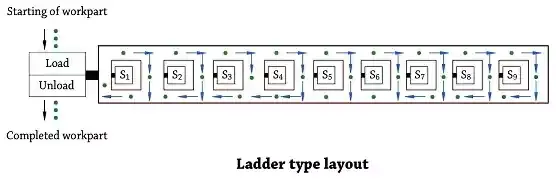
• Ladder layout
• Carousel layout
• Robot centered cell
• Open field layout.
In-line layout:
• An Automated guided vehicle is most efficient when the movement is in straight- lines along the AC-V path in a single-row machine layout.• Machines are arranged only on one side of AGV path, and in double row machine layout, machines are arranged on both sides.
Loop layout:
• The loop layout uses conveyor systems that allow unidirectional flow of parts around the loop.• A secondary material handling system is provided at a workstation which permits the flow of parts without any obstruction.
Ladder layout:
• Ladder type layout consists of rungs on which workstations are located.• This reduces the average travel distance there by reducing the transfer time between workstations.
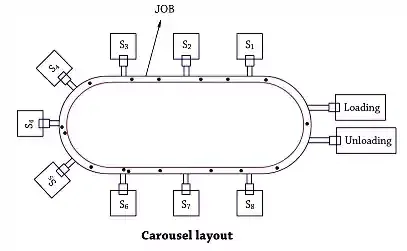
Carousel layout:
• In the Carousel layout configuration, parts flow in one direction around the loop The load, unload stations are placed at one end of loop.Robot centered cell:
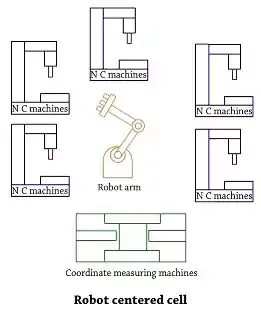
• If a handling robot is used in a flexible manufacturing system cell , the machines are laid out in a circle, such a layout is called circular layout.Open field layout:
• The open field layout is also an adoption of the loop configuration.• The open field layout consists of loops and ladders organized to achieve the desired processing requirements.
• This is used for the processing of a large family of parts. The number of different machines may be limited, and the parts are routed to different workstations depending on availability of machines.
Working of FMS:
• The raw workpiece are normally stored in automated storage and retrieval system [ASRS].• The raw workpiece enters the system from ASRS called loading of work part.
• Then the workpiece enters to the various machine stations for various machining operations.
• If the particular machine centre is busy.
• The workpiece will be diverted to any other idle machine.
• For this artificial intelligence is used.
• FMS consists of several material handling systems that have to be synchronized with the machine operation.
• Normally conveyors, automatic pallet changers, AGV’s are used for handling system.
• On completion of all machining operations the workpiece enters the chip removal and washing stations.
• The cleaned workpiece enters the inspection station.
• Using a robot, the workpiece will be moved to the coordinate measuring machine [CMM].
• Here the parts are inspected as per given specifications.
• After inspection, all accepted workpiece enter the assembly station.
• Here the assembly of work parts is done.
• The assembled work parts will be transported to the storage racks.
• In FMS, a central coolant system supplies the coolant to various machines.
• The FMS computer system consists of a central computer and micro computers.
• These control the individual machines and other components.
• The computer system is interfaced to the work stations, material handling system and other hard ware components.
• The central computer co-ordinates the activities of the components to achieve smooth overall operation of the system.
Advantages of FMS:
●
Reduced work in process.
●
Increased machine
utilization.
●
Increased production
flexibility.
●
Increased system
reliability.
●
Better management
control.
●
Reduced direct and
indirect labour.
●
Reduced manufacturing
lead-time
●
Consistent and better
quality.
● Reduced
inventory.
●
FMS are compatible with
CIM.
●
FMS reduced number of
tools and machines
●
Quicker response to
market changes.
Disadvantages of FMS:
●
Due to increased
complexity and cost, an FMS also requires a longer planning and development
period than traditional manufacturing equipment.
●
Very high start-up cost.
●
Limited ability to adapt
changes in product.
●
It is difficult to
position the component accurately and it needs more process time.
●
Not economical for low
production rates.
●
Unemployment problem
will arise.
END
















0 Comments